

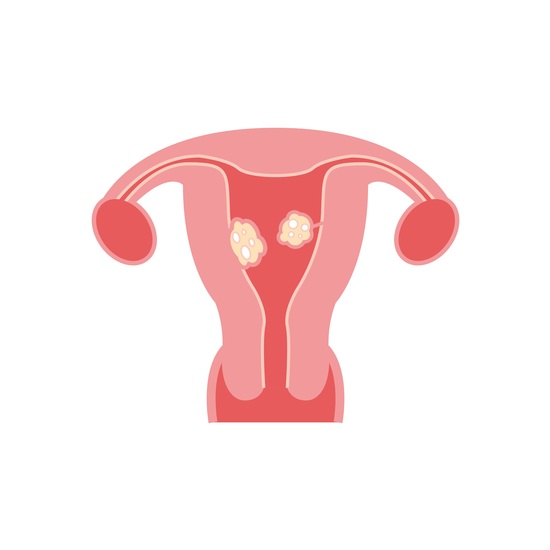
Fibroids are abnormal growths which develop in or on the uterus. They are generally non-cancerous with most women not even aware of their presence in their body – i.e., they are symptomless. Fibroids are believed to be caused by a combination of factors including hormonal imbalances, pregnancy and family history. It’s estimated that about 70-80% of females get them before the age of 50 years.
Fibroids can be classified depending on their location:
The amazing thing about fibroids is that some are completely symptomless while others may cause extreme pain and prolonged and very heavy periods. They can also create pressure on other organs and the spine, affect your sex life and even cause you to urinate frequently. Sometimes their size can interfere in childbirth and create fertility issues too.
So what’s the treatment you ask? Treatment is based on the size and location of the fibroid as well as the health of the woman. It involves the use of medications to shrink the size of the fibroids to more manageable levels. To help in controlling pain and bleeding issues, you might be given birth control pills, IUDs or painkillers. However, these won’t eliminate the fibroids.
In cases of large multiple fibroids, a surgical incision of the abdomen is done to remove them. It can also be done laparoscopically. In case there is no improvement, a hysterectomy may be needed.
Some newer minimally invasive procedures that use high-energy, high-frequency sound waves, microwaves, electric current or lasers can all be employed to destroy these fibroids too. Alternatively, they can be destroyed by freezing through cryomyolysis.